[Linux]u-boot_2014移植(一)分析启动流程
[Linux]u-boot_2014移植(二)分析启动流程
艾恩凝
2021/6/4
一)分析u-boot.lds
本来首先分析启动流程,这个文件需要编译生成出来,第一步是创建单板,生成这个文件在,主目录文件夹下
1OUTPUT_FORMAT("elf32-littlearm", "elf32-littlearm", "elf32-littlearm")
2OUTPUT_ARCH(arm)
3ENTRY(_start)
4SECTIONS
5{
6 . = 0x00000000;
7 . = ALIGN(4);
8 .text :
9 {
10 *(.__image_copy_start)
11 arch/arm/cpu/arm920t/start.o (.text*)
12 board/samsung/smdk2440/built-in.o(.text*)
13 arch/arm/cpu/built-in.o (.text*)
14 *(.text*)
15 }
16 . = ALIGN(4);
17 .rodata : { *(SORT_BY_ALIGNMENT(SORT_BY_NAME(.rodata*))) }
18 . = ALIGN(4);
19 .data : {
20 *(.data*)
21 }
22 . = ALIGN(4);
23 . = .;
24 . = ALIGN(4);
25 .u_boot_list : {
26 KEEP(*(SORT(.u_boot_list*)));
27 }
28 . = ALIGN(4);
29 .image_copy_end :
30 {
31 *(.__image_copy_end)
32 }
33 .rel_dyn_start :
34 {
35 *(.__rel_dyn_start)
36 }
37 .rel.dyn : {
38 *(.rel*)
39 }
40 .rel_dyn_end :
41 {
42 *(.__rel_dyn_end)
43 }
44 _end = .;
45 . = ALIGN(4096);
46 .mmutable : {
47 *(.mmutable)
48 }
49 .bss_start __rel_dyn_start (OVERLAY) : {
50 KEEP(*(.__bss_start));
51 __bss_base = .;
52 }
53 .bss __bss_base (OVERLAY) : {
54 *(.bss*)
55 . = ALIGN(4);
56 __bss_limit = .;
57 }
58 .bss_end __bss_limit (OVERLAY) : {
59 KEEP(*(.__bss_end));
60 }
61 .dynsym _end : { *(.dynsym) }
62 .dynbss : { *(.dynbss) }
63 .dynstr : { *(.dynstr*) }
64 .dynamic : { *(.dynamic*) }
65 .plt : { *(.plt*) }
66 .interp : { *(.interp*) }
67 .gnu : { *(.gnu*) }
68 .ARM.exidx : { *(.ARM.exidx*) }
69 .gnu.linkonce.armexidx : { *(.gnu.linkonce.armexidx.*) }
70}
71
上面会有很多符号,最熟悉的便是_start、__bss_end、__bss_base 等,这些符号用来表示地址,从上面可以看到程序入口是 _start 这个全局符号在arch/arm/cpu/arm920t/start.S 这个汇编文件中。
二)start.S
1)设置异常向量表
1.globl _start
2_start: b start_code
3 ldr pc, _undefined_instruction
4 ldr pc, _software_interrupt
5 ldr pc, _prefetch_abort
6 ldr pc, _data_abort
7 ldr pc, _not_used
8 ldr pc, _irq
9 ldr pc, _fiq
10
11_undefined_instruction: .word undefined_instruction
12_software_interrupt: .word software_interrupt
13_prefetch_abort: .word prefetch_abort
14_data_abort: .word data_abort
15_not_used: .word not_used
16_irq: .word irq
17_fiq: .word fiq
18
19 .balignl 16,0xdeadbeef
从上面看,开机复位后就跳转到start_code 开始执行,其他的是处理一些异常
2)start_code分析
1start_code:
2 /*
3 * set the cpu to SVC32 mode
4 */
5 mrs r0, cpsr
6 bic r0, r0, #0x1f
7 orr r0, r0, #0xd3
8 msr cpsr, r0
9
10#if defined(CONFIG_AT91RM9200DK) || defined(CONFIG_AT91RM9200EK)
11 /*
12 * relocate exception table
13 */
14 ldr r0, =_start
15 ldr r1, =0x0
16 mov r2, #16
17copyex:
18 subs r2, r2, #1
19 ldr r3, [r0], #4
20 str r3, [r1], #4
21 bne copyex
22#endif
23
24#ifdef CONFIG_S3C24X0
25 /* turn off the watchdog */
26
27# if defined(CONFIG_S3C2400)
28# define pWTCON 0x15300000
29# define INTMSK 0x14400008 /* Interrupt-Controller base addresses */
30# define CLKDIVN 0x14800014 /* clock divisor register */
31#else
32# define pWTCON 0x53000000
33# define INTMSK 0x4A000008 /* Interrupt-Controller base addresses */
34# define INTSUBMSK 0x4A00001C
35# define CLKDIVN 0x4C000014 /* clock divisor register */
36# endif
37
38 ldr r0, =pWTCON
39 mov r1, #0x0
40 str r1, [r0]
41
42 /*
43 * mask all IRQs by setting all bits in the INTMR - default
44 */
45 mov r1, #0xffffffff
46 ldr r0, =INTMSK
47 str r1, [r0]
48# if defined(CONFIG_S3C2410)
49 ldr r1, =0x3ff
50 ldr r0, =INTSUBMSK
51 str r1, [r0]
52# endif
53
54 /* FCLK:HCLK:PCLK = 1:2:4 */
55 /* default FCLK is 120 MHz ! */
56 ldr r0, =CLKDIVN
57 mov r1, #3
58 str r1, [r0]
59#endif /* CONFIG_S3C24X0 */
60
61 /*
62 * we do sys-critical inits only at reboot,
63 * not when booting from ram!
64 */
65#ifndef CONFIG_SKIP_LOWLEVEL_INIT
66 bl cpu_init_crit
67#endif
68
69 bl _main
上面部分主要做了
- 设置svc管理模式
- 关闭看门狗
- 关闭中断
- 设置时钟频率
- cpu_init_crit 禁用Cache和MMU,
- cpu_init_crit 中的 lowlevel_init 1)初始化存储控制器 2) _TEXT_BASE 为CONFIG_SYS_TEXT_BASE
- 跳转到 _main
3)_main分析
1.设置栈
1#if defined(CONFIG_SPL_BUILD) && defined(CONFIG_SPL_STACK)
2 ldr sp, =(CONFIG_SPL_STACK)
3#else
4 ldr sp, =(CONFIG_SYS_INIT_SP_ADDR)
5#endif
6 bic sp, sp, #7 /* 8-byte alignment for ABI compliance */
7 sub sp, sp, #GD_SIZE /* allocate one GD above SP */
8 bic sp, sp, #7 /* 8-byte alignment for ABI compliance */
9 mov r9, sp /* GD is above SP */
10 mov r0, #0
2.board_init_f 单板初始化
c函数数组init_sequence_f
1static init_fnc_t init_sequence_f[] = {
2#ifdef CONFIG_SANDBOX
3 setup_ram_buf,
4#endif
5 setup_mon_len,
6 setup_fdt,
7 trace_early_init,
8#if defined(CONFIG_MPC85xx) || defined(CONFIG_MPC86xx)
9 /* TODO: can this go into arch_cpu_init()? */
10 probecpu,
11#endif
12 arch_cpu_init, /* basic arch cpu dependent setup */
13#ifdef CONFIG_X86
14 cpu_init_f, /* TODO(sjg@chromium.org): remove */
15# ifdef CONFIG_OF_CONTROL
16 find_fdt, /* TODO(sjg@chromium.org): remove */
17# endif
18#endif
19 mark_bootstage,
20#ifdef CONFIG_OF_CONTROL
21 fdtdec_check_fdt,
22#endif
23#if defined(CONFIG_BOARD_EARLY_INIT_F)
24 board_early_init_f,
25#endif
26 /* TODO: can any of this go into arch_cpu_init()? */
27#if defined(CONFIG_PPC) && !defined(CONFIG_8xx_CPUCLK_DEFAULT)
28 get_clocks, /* get CPU and bus clocks (etc.) */
29#if defined(CONFIG_TQM8xxL) && !defined(CONFIG_TQM866M) \
30 && !defined(CONFIG_TQM885D)
31 adjust_sdram_tbs_8xx,
32#endif
33 /* TODO: can we rename this to timer_init()? */
34 init_timebase,
35#endif
36#ifdef CONFIG_ARM
37 timer_init, /* initialize timer */
38#endif
39#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_ALLOC_DPRAM
40#if !defined(CONFIG_CPM2)
41 dpram_init,
42#endif
43#endif
44#if defined(CONFIG_BOARD_POSTCLK_INIT)
45 board_postclk_init,
46#endif
47#ifdef CONFIG_FSL_ESDHC
48 get_clocks,
49#endif
50 env_init, /* initialize environment */
51#if defined(CONFIG_8xx_CPUCLK_DEFAULT)
52 /* get CPU and bus clocks according to the environment variable */
53 get_clocks_866,
54 /* adjust sdram refresh rate according to the new clock */
55 sdram_adjust_866,
56 init_timebase,
57#endif
58 init_baud_rate, /* initialze baudrate settings */
59 serial_init, /* serial communications setup */
60 console_init_f, /* stage 1 init of console */
61#ifdef CONFIG_SANDBOX
62 sandbox_early_getopt_check,
63#endif
64#ifdef CONFIG_OF_CONTROL
65 fdtdec_prepare_fdt,
66#endif
67 display_options, /* say that we are here */
68 display_text_info, /* show debugging info if required */
69#if defined(CONFIG_8260)
70 prt_8260_rsr,
71 prt_8260_clks,
72#endif /* CONFIG_8260 */
73#if defined(CONFIG_MPC83xx)
74 prt_83xx_rsr,
75#endif
76#ifdef CONFIG_PPC
77 checkcpu,
78#endif
79#if defined(CONFIG_DISPLAY_CPUINFO)
80 print_cpuinfo, /* display cpu info (and speed) */
81#endif
82#if defined(CONFIG_MPC5xxx)
83 prt_mpc5xxx_clks,
84#endif /* CONFIG_MPC5xxx */
85#if defined(CONFIG_DISPLAY_BOARDINFO)
86 checkboard, /* display board info */
87#endif
88 INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_INIT
89#if defined(CONFIG_MISC_INIT_F)
90 misc_init_f,
91#endif
92 INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
93#if defined(CONFIG_HARD_I2C) || defined(CONFIG_SYS_I2C)
94 init_func_i2c,
95#endif
96#if defined(CONFIG_HARD_SPI)
97 init_func_spi,
98#endif
99#ifdef CONFIG_X86
100 dram_init_f, /* configure available RAM banks */
101 calculate_relocation_address,
102#endif
103 announce_dram_init,
104 /* TODO: unify all these dram functions? */
105#ifdef CONFIG_ARM
106 dram_init, /* configure available RAM banks */
107#endif
108#ifdef CONFIG_PPC
109 init_func_ram,
110#endif
111#ifdef CONFIG_POST
112 post_init_f,
113#endif
114 INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
115#if defined(CONFIG_SYS_DRAM_TEST)
116 testdram,
117#endif /* CONFIG_SYS_DRAM_TEST */
118 INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
119
120#ifdef CONFIG_POST
121 init_post,
122#endif
123 INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
124 /*
125 * Now that we have DRAM mapped and working, we can
126 * relocate the code and continue running from DRAM.
127 *
128 * Reserve memory at end of RAM for (top down in that order):
129 * - area that won't get touched by U-Boot and Linux (optional)
130 * - kernel log buffer
131 * - protected RAM
132 * - LCD framebuffer
133 * - monitor code
134 * - board info struct
135 */
136 setup_dest_addr,
137#if defined(CONFIG_LOGBUFFER) && !defined(CONFIG_ALT_LB_ADDR)
138 reserve_logbuffer,
139#endif
140#ifdef CONFIG_PRAM
141 reserve_pram,
142#endif
143 reserve_round_4k,
144#if !(defined(CONFIG_SYS_ICACHE_OFF) && defined(CONFIG_SYS_DCACHE_OFF)) && \
145 defined(CONFIG_ARM)
146 reserve_mmu,
147#endif
148#ifdef CONFIG_LCD
149 reserve_lcd,
150#endif
151 reserve_trace,
152 /* TODO: Why the dependency on CONFIG_8xx? */
153#if defined(CONFIG_VIDEO) && (!defined(CONFIG_PPC) || defined(CONFIG_8xx)) \
154 && !defined(CONFIG_ARM) && !defined(CONFIG_X86)
155 reserve_video,
156#endif
157 reserve_uboot,
158#ifndef CONFIG_SPL_BUILD
159 reserve_malloc,
160 reserve_board,
161#endif
162 setup_machine,
163 reserve_global_data,
164 reserve_fdt,
165 reserve_stacks,
166 setup_dram_config,
167 show_dram_config,
168#ifdef CONFIG_PPC
169 setup_board_part1,
170 INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
171 setup_board_part2,
172#endif
173 setup_baud_rate,
174 display_new_sp,
175#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_EXTBDINFO
176 setup_board_extra,
177#endif
178 INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
179 reloc_fdt,
180 setup_reloc,
181#if !defined(CONFIG_ARM) && !defined(CONFIG_SANDBOX)
182 jump_to_copy,
183#endif
184 NULL,
185};
- board_early_init_f函数:完成ARM的时钟频率和IO的设置
- timer_init函数:完成定时器4的设置
- env_init函数:完成环境变量的设置
- init_baud_rate函数:完成波特率的设置
- serial_init函数:完成串口通讯的设置
- console_init_f函数:完成第一阶段的控制台初始化
- display_banner函数:用来打印输出一些信息
- print_cpuinfo函数:输出CPU信息
- dram_init函数:用来配置SDRAM的大小。
SDRAM地址分配
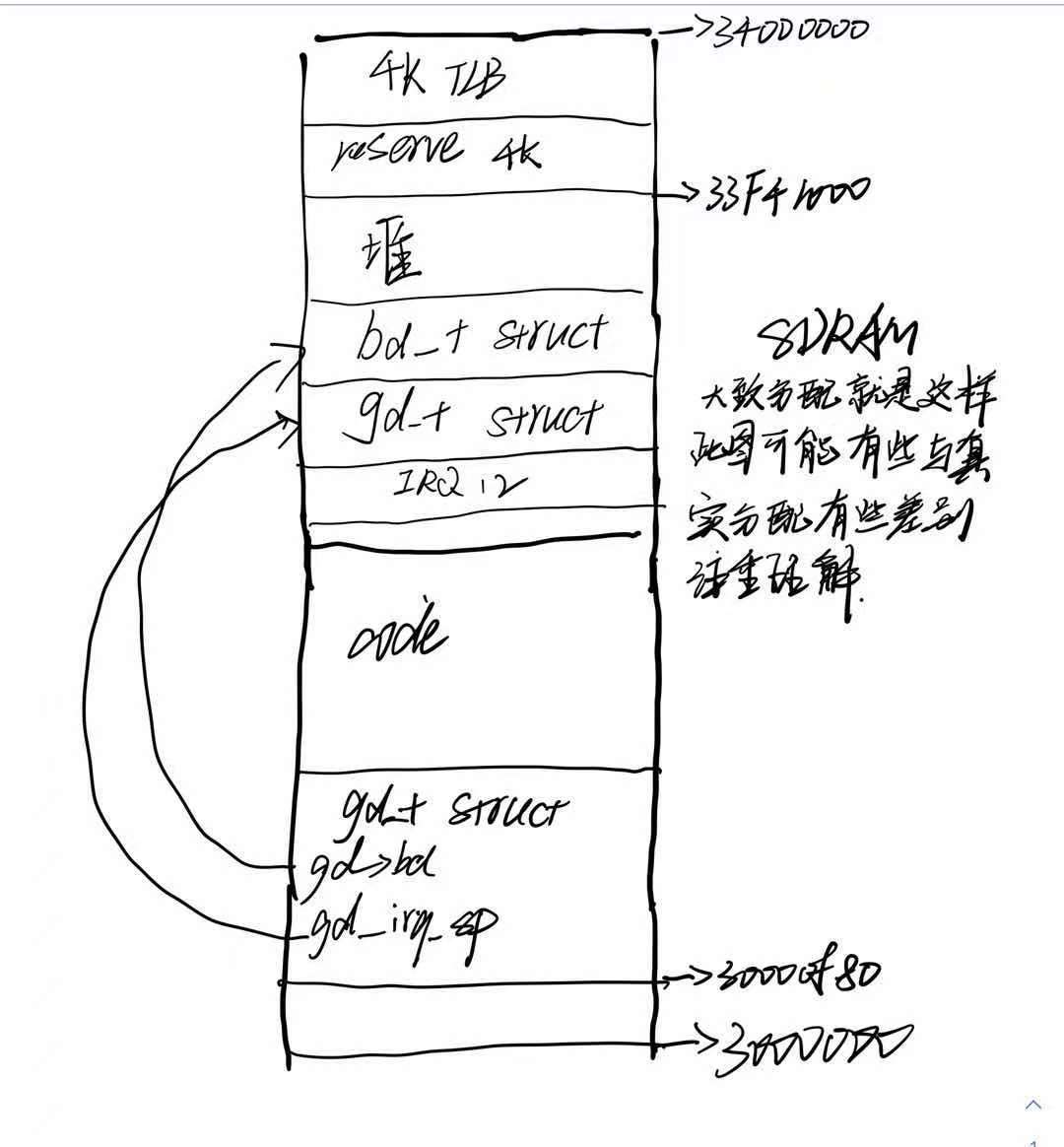
2016
重定位
调用C函数jump_to_copy,函数中relocate_code进行重定位
- 从NOR FLASH把代码复制到SDRAM
- 程序的链接地址是0,访问全局变量、静态变量、调用函数时是使"基于0地址编译得到的地址"
- 程序里有些地址在链接时不能确定,要到运行前才能确定:fixabs
3.清除bss段
1/*
2 * Set up intermediate environment (new sp and gd) and call
3 * relocate_code(addr_moni). Trick here is that we'll return
4 * 'here' but relocated.
5 */
6
7 ldr sp, [r9, #GD_START_ADDR_SP] /* sp = gd->start_addr_sp */
8 bic sp, sp, #7 /* 8-byte alignment for ABI compliance */
9 ldr r9, [r9, #GD_BD] /* r9 = gd->bd */
10 sub r9, r9, #GD_SIZE /* new GD is below bd */
11
12 adr lr, here
13 ldr r0, [r9, #GD_RELOC_OFF] /* r0 = gd->reloc_off */
14 add lr, lr, r0
15 ldr r0, [r9, #GD_RELOCADDR] /* r0 = gd->relocaddr */
16 b relocate_code
17here:
18
19/* Set up final (full) environment */
20
21 bl c_runtime_cpu_setup /* we still call old routine here */
22
23 ldr r0, =__bss_start /* this is auto-relocated! */
24 ldr r1, =__bss_end /* this is auto-relocated! */
25
26 mov r2, #0x00000000 /* prepare zero to clear BSS */
27
28clbss_l:cmp r0, r1 /* while not at end of BSS */
29 strlo r2, [r0] /* clear 32-bit BSS word */
30 addlo r0, r0, #4 /* move to next */
31 blo clbss_l
32
33 bl coloured_LED_init
34 bl red_led_on
4.board_init_r
init_sequence_r
执行init_sequence_r数组函数进行最后初始化
1.1.1 调用C函数initr_nand:
1.1.1.1 调用C函数nand_init初始化NAND FLASH
1.1.1.1.1 调用C函数nand_init_chip选中NAND FLASH
1.1.1.1.1.1调用C函数board_nand_init初始化时序
1.1.1.1.1.2 调用C函数nand_scan扫描NAND FALSH
1.1.1.1.1.2.1 调用C函数nand_scan_ident
1.1.1.1.1.2.1.1 调用C函数nand_set_defaults设置默认功能
1.1.1.1.1.2.1.1.1 C函数nand_command,发命令or来发列地址、行地址
1.1.1.1.1.2.1.2 调用C函数nand_get_flash_type读出NAND FALSH类型
1.1.1.1.1.3 调用C函数nand_register注册NAND FALSH
1.1.2 调用C函数initr_env初始化环境参数
1.1.2.1 调用C函数set_default_env设置默认环境变量
1.1.3 调用C函数initr_net初始化网卡
1.1.3.1 调用C函数eth_initialize
1.1.3.1.1 调用C函数board_eth_init初始化CS8900网卡
1.1.4 调用C函数run_main_loop,这就是最后的循环命令行窗口那
主要工作就是
- 设置单板id
- 初始化串口
- 初始化堆内存
- 初始化外部存储设备
- 环境变量的重定位
- 网卡初始化
- 进入main_loop循环
三)end
分析终于结束了,这就是大体的uboot启动流程
u-boot移植系列目录
下一篇 [Linux]u-boot_2014移植(二)创建单板
 评论
评论